Modular repair equipment and tool stand for ships SHISTE1-1
TECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION
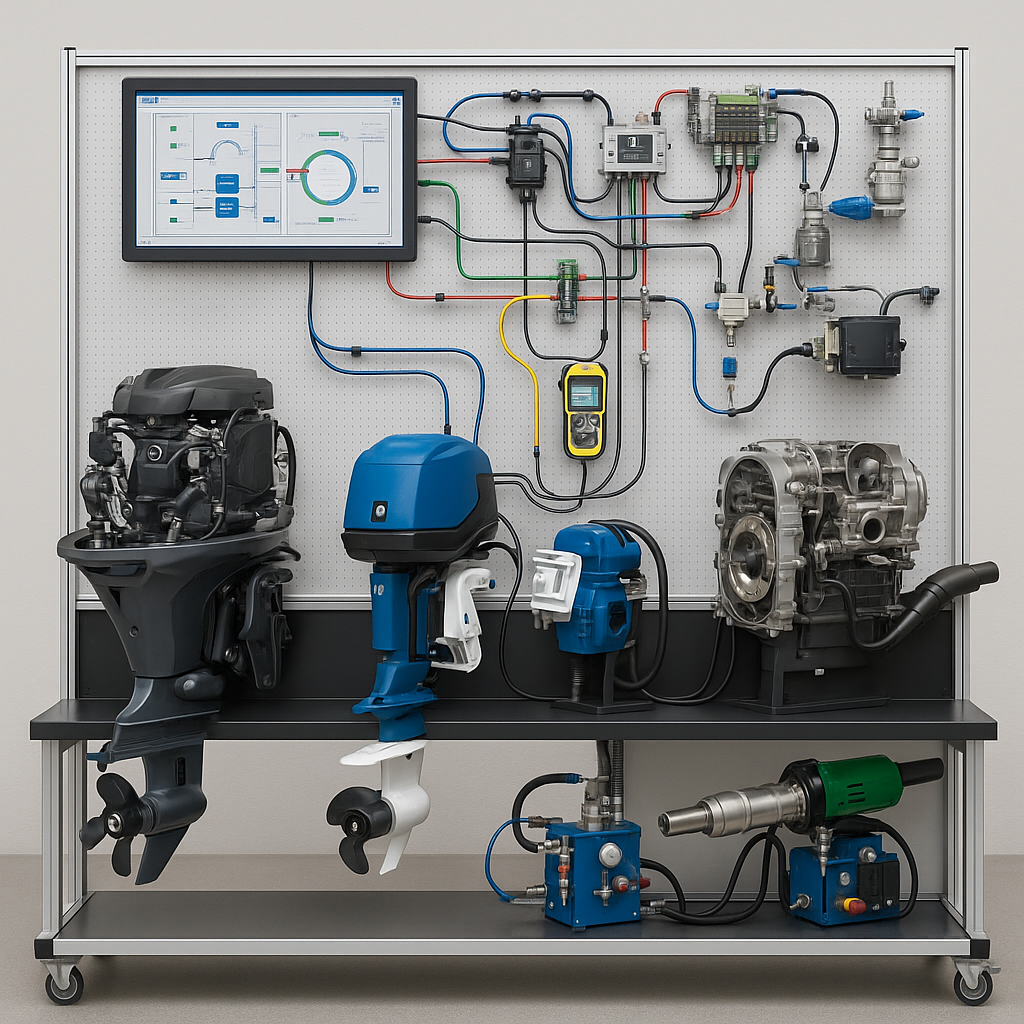
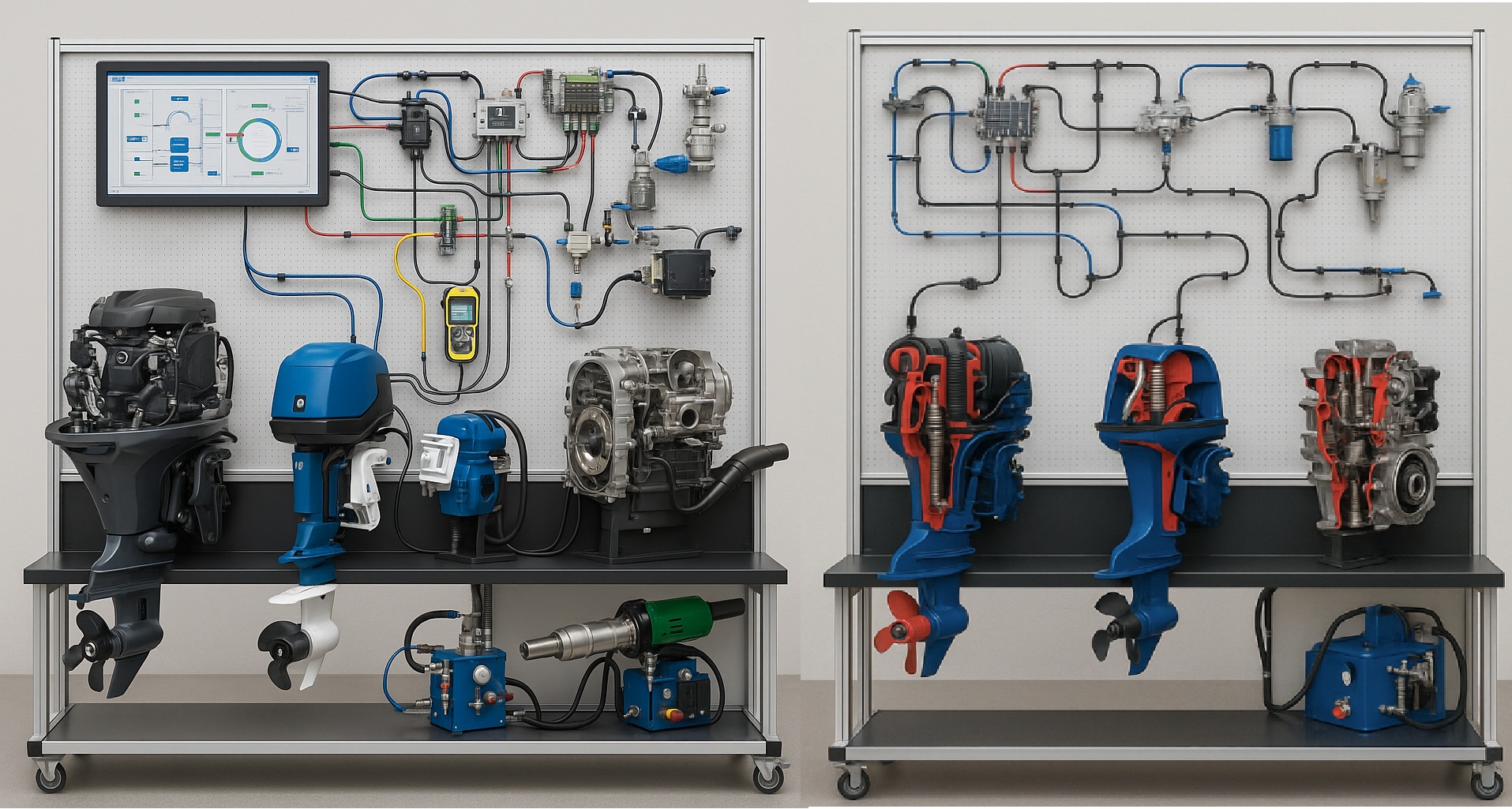
Modular repair equipment and tool stand for ships (inland waterway vessels) with SCADA control and fault simulation from Android/iOS systems, consisting of working engine modules (3 different types), ultrasonic (engine, gearbox, hydraulic systems testing) module (used with engine modules), extruder (for welding plastic ship/boat hulls), a ship hydraulics (150 bar) and control systems repair module, and inland waterway vessel engine sections with a ship repair tool kit (SHISTE1-1)
GENERAL INFORMATION
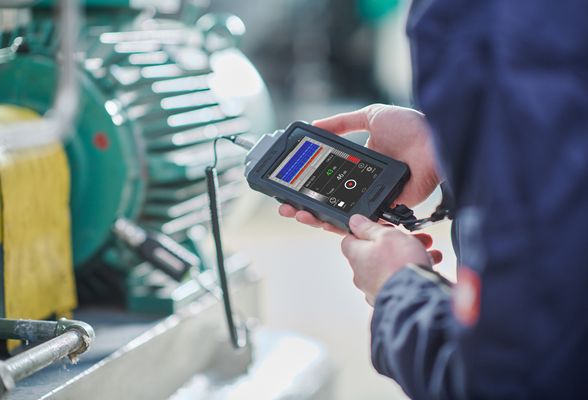
The modular ship repair equipment and tool stand is a comprehensive training system designed for the maintenance, diagnostics, and repair of inland waterway vehicle engines, hydraulics, transmissions, and control systems. The system combines mechanical, electronic, pneumatic, and hydraulic modules into a single integrated stand controlled via a SCADA environment, and the training processes are supplemented by MatLab electronics simulation and fault simulation from Android/iOS mobile systems. The stand covers the entire repair and diagnostics cycle – from engine testing, emissions analysis, and electrical component testing to plastic welding, hydraulic and transmission system repair, and electronics diagnostics. Using an ultrasonic module, students can test and identify simulated faults in diesel, gasoline, and electric boat engines. Students learn how to work with non-destructive technology, where faults are identified without disassembly, using ultrasonic systems. With the help of an ultrasonic system, it is possible to identify faults in the engine and gearbox of an inland waterway transport vehicle (IWT) and perform a technical inspection to determine the wear and tear of the engine, gearbox, and mechanical drives and what further repairs these systems require. The software integrates fault simulation into any IWT engine or gearbox, encouraging students to respond to faults and eliminate them. Faults are simulated on mobile phones and tablets running Android or iOS systems. With the help of the ship’s hydraulics and control systems repair module, students are not only introduced to ship hydraulic circuits, but also taught about all hydraulic systems (from simple hydraulic systems to ship steering systems). Students use VVTP engine cross-sections to understand engine assembly and can more easily work on real engines, disassembling and reassembling them. The entire system is integrated with SCADA control, which simulates all engines, ultrasonic equipment, and repair equipment in the SCADA system, allowing students to see all circuits and their parameters.
Functional areas and objectives
- Analysis and practical testing of ship engines (gasoline, diesel, and electric).
- Simulation of the operation and malfunctions of transmission and hydraulic systems.
- Application of hull plastic repair technologies using an extruder.
- Diagnostics of electrical and electronic systems (ignition, charging, sensors, drives).
- Exhaust gas analysis and compliance with environmental standards.
- Integrated data monitoring, analysis, and diagnostics in the SCADA control environment.
- Fault simulation, controlled remotely via Android/iOS applications.
- MatLab simulation, allowing the creation and testing of electrical circuit algorithms.
- In-depth analysis of systems by understanding the structure shown in the cross-sections of VVTP engines and gearboxes and performing repairs on an analog engine similar to a real VVTP engine.
- Introduction to non-destructive technologies and working with ultrasound.
- A complete production line is presented, where all three engines used in VVTP can be seen.
Components:
The training stand consists of integrated modules that work together and are connected via SCADA and fault simulation from Android/iOS systems:
- Engine modules – gasoline, diesel, and electric boat engines used for real diagnostics, repair, and operational testing training. These engines are connected to the SCADA system and fault simulation, as well as an ultrasonic module for fault detection.
- Gearbox and hydraulics testing module – connected to engines, designed for analyzing the operation of transmission and hydraulic systems.
- Ship hydraulics module, which allows you to create ship control system circuits and test them, as well as simulate faults and eliminate them.
- Extruder – for plastic welding and ship/boat hull repair work.
- Hydraulic and control system repair module – allows you to simulate, repair, and test ship hydraulic and control circuits.
- Inland waterway vessel engine cross-sections and repair tool kit – used for structural analysis and practical repair work.
- Exhaust gas analysis stand (IDAS) – for emission control. Diesel and gasoline engines are connected to IDAS and diagnosed. Faults are also simulated when the fuel composition is changed and the exhaust gas concentration increases, then the student must measure the concentration level, determine whether it is exceeded, and if it is exceeded, make a decision and perform repair work, as well as perform an IDAS measurement after the repair work.
- Smoke extraction system – with automatic air vents and a rail for a safe working environment.
- Starter/generator test bench – for testing electrical systems. This model is connected to an engine module and allows different starter and generator systems to be tested so that students can familiarize themselves with the parameters and perform fault repairs.
- Tool trolleys and professional tools – for performing work. All tools are adapted to the training modules and allow all tasks to be performed. The use of tools is described in the training material, which provides practical visual, textual, and video examples of how to perform tasks according to the manufacturer’s documentation. Similarly, a compressed air system with a screw compressor and a set of pneumatic tools is used for mechanical work, and a pneumatic-hydraulic press is used for the assembly and disassembly of units.
- Multifunctional battery charger/diagnostic charger – for power supply and testing. Designed to charge VVTP batteries that will be used in the training classroom.
- Database – for ship system diagnostics. A professional database with repair examples, diagrams, and repair information is provided. All information is provided together with the training material.
- Biological (environmentally friendly) parts washer and ultrasonic cleaning tank – for component maintenance. Students disassemble VVTP engines and gearboxes and wash the parts using a biological ship part washer (contributing to green transformation), and then the mechanisms are re-lubricated with ship mechanism grease and reassembled into the engine structure.
- With the help of a sensor, gear, ignition system, sensor, and electronic circuit module with an oscilloscope, students analyze electrical circuits and learn how to connect them to VVTP engines.
TRAINING ACTIVITIES AND OPPORTUNITIES (During training, students):
- Perform engine start-up, diagnostics, and maintenance work.
- Test transmission and hydraulic systems and identify faults.
- Practice plastic welding technology for ship hull repair.
- Use electrical and electronic training stands, perform diagnostics of ignition, charging, and sensor systems.
- Perform emission measurements and analyze environmental indicators.
- Operates the SCADA system, identifies faults generated in real time.
- Works with the MatLab model, analyzing the operation of electrical circuits.
- Acquires skills in working with pneumatic, hydraulic, electrical, and electronic equipment.
COMPETENCIES THAT STUDENTS WILL ACQUIRE:
- Maintenance and repair of inland waterway vessel engines, transmissions, hydraulic and electronic systems.
- Fault diagnosis using both practical modules and the SCADA software environment.
- Application of plastic hull welding and repair technologies.
- Analysis, diagnostics, and simulation of electrical and electronic systems using MatLab.
- Working with pneumatic, hydraulic, and mechanical equipment.
- Ability to use modern databases, analysis tools, and simulations.
- Application of digital technologies and innovations in inland waterway transport supervision.